4 sampling methods in statistics|four types of sampling methods : discounter There are two primary types of sampling methods that you can use in your research: Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. Non-probability .
web16 de abr. de 2022 · Karsa broke the LPL record for the highest number of kills in a single game for a jungler in today’s 2022 Spring Split Playoffs matchup between Victory Five and JD Gaming. He boasted a KDA of 17 .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBA Betclic é uma das principais marcas de apostas online em Portugal e, por isso, não é de estranhar que a Betclic app apresente novidades em 2024. Tem à disposição versões da app que são indicadas tanto para dispositivos Android como iOS, com muitas vantagens para quem gosta de apostas desportivas.
Example:A researcher stands in front of a library during the day and polls people that happen to walk by. Drawback: Location and time of day will affect the results. More than likely, the sample will suffer from undercoverage biassince certain people (e.g. those who work during the day) will not be represented as much . See moreExample:A radio host asks listeners to go online and take a survey on his website. Drawback: People who voluntarily respond will likely have stronger opinions (positive or negative) than the . See moreExample:Researchers are conducting a study of individuals with rare diseases, but it’s difficult to find individuals who actually have the disease. . See moreExample:Researchers want to know about the opinions that individuals in a city have about a potential new rock climbing gym being placed in the city square so they purposely seek out . See more
Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias. Sampling methods. Sampling methods review. Samples and surveys. There are two primary types of sampling methods that you can use in your research: Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. Non-probability .
A sample is the subset of the population that you actually measure, test, or evaluate and base your results. Sampling methods are how you obtain your sample. Before beginning your study, carefully define the . Sampling methods or sampling techniques in research are statistical methods for selecting a sample representative of the whole population to study the population’s characteristics.
spigen air skin drop test
OpenStax. Sampling. Gathering information about an entire population often costs too much or is virtually impossible. Instead, we use a sample of the population. A sample should have the same characteristics as .
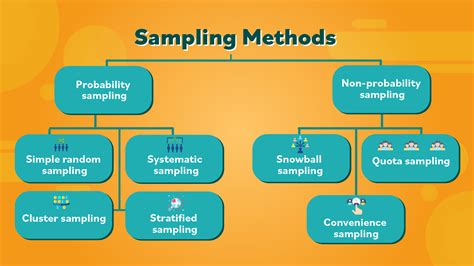
You’ll come across many terms in statistics that define different sampling methods: simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified random sampling and cluster sampling. How to tell the difference between the . There are two types of sampling methods: Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. It minimises the risk of selection bias. Non-probability . There are four commonly used types of probability sampling designs: Simple random sampling. Stratified sampling. Systematic sampling. Cluster sampling. Simple .
Systematic random sample. Definition: Put every member of a population into some order. Choosing a random starting point and select every nth member to be in the sample. Example: A teacher puts students in .
Choose the sampling method: Select an appropriate sampling method based on the research question, characteristics of the population, and available resources. Determine the sample size: Determine the desired sample size based on statistical considerations such as margin of error, confidence level, or power analysis. Common non-probability sampling methods include convenience sampling, voluntary response sampling, purposive sampling, snowball sampling, and quota sampling. What is sampling bias? Sampling bias .Stratified sampling: The population is divided into smaller groups, or “strata,” that share a characteristic.People from each smaller group are randomly selected to form the sample. For example, if we want to know the top favorite food among .
Another sampling method is cluster sampling, in which the population is divided into groups, and one or more groups are randomly selected to be in the sample. Cluster sampling In cluster sampling , the population is divided into subgroups (clusters), and a set of subgroups are selected to be in the sample This page titled 1.2: Sampling Methods is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Kathryn Kozak via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform. Learn about the types of samples such as biased samples, convenience samples, voluntary response samples, unbiased samples, and sampling methods such as stra.
Data sampling is a statistical method that involves selecting a part of a population of data to create representative samples. The fundamental aim is to draw conclusions about the entire population without having to engage with every individual data point, thus saving time, resources, and effort while still achieving accurate results.
The Practice of Statistics for the AP Exam . Preview. busi stats ch 12 and 13. 16 terms. Ali6276. Preview. 4.1 Sampling Method Examples (v2) Teacher 19 terms. MrLamP10. Preview. MS 2050 Exam 1. 35 terms. kaylametz0. Preview. Stats II notes. 26 terms. dustychr. Preview. PSYC 210- Sampling Theory. 16 terms. trucp. Preview. AP Statistics .What is sampling? Sampling is a technique of selecting individual members or a subset of the population to make statistical inferences from them and estimate the characteristics of the whole population. Different sampling methods are widely used by researchers in market research so that they do not need to research the entire population to collect actionable insights.
Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling. Proper sampling ensures representative, generalizable, and . Another sampling method is cluster sampling, in which the population is divided into groups, and one or more groups are randomly selected to be in the sample. Cluster sampling In cluster sampling , the population is divided into subgroups (clusters), and a set of subgroups are selected to be in the sample
When to use simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is used to make statistical inferences about a population. It helps ensure high internal validity: randomization is the best method to reduce the impact of potential confounding variables.. In addition, with a large enough sample size, a simple random sample has high external validity: .Non-probability sampling methods. Non-probability sampling methods are convenient and cost-savvy. But they do not allow to estimate the extent to which sample statistics are likely to vary from population parameters. Whereas probability sampling methods allows that kind of analysis. Following are the types of non-probability sampling methods .
sampling techniques in statistics examples
This section will describe a few of the most common methods. There are several different methods of random sampling. In each form of random sampling, each member of a population initially has an equal chance of being selected for the sample. Each method has pros and cons. The easiest method to describe is called a simple random sample. In a .3.4 statistical significance. 14 terms. cmvukovich. Preview. Midterm 1 Review. 60 terms. kyrajacksonscholar. Preview. HTH 320 Exam 2. 36 terms. Erin_Williams390. Preview. AP Stat 5.1. . a method of sampling that relies on chance or a selection method so that every element of the sampling frame has a known probability of being selected. Simple .Types Of Sampling Methods. Here we will learn about sampling methods, including random sampling, non-random, stratified sampling, systematic sampling and capture/recapture. There are also types of sampling methods . Specify the method for taking measurements or making observations. Determine if you are taking a census or sample. If taking a sample, decide on the sampling method. Collect the data. Use appropriate .
spigen bumper case drop test
Statistics is all about forming questions and gathering data to explore those questions. This unit connects these questions to aspects of research design, including sampling and survey methods, observational studies, and basic experiment design.
Sampling is one of the most important factors which determines the accuracy of a study. This article review the sampling techniques used in research including Probability sampling techniques .Non-probability sampling methods are used in qualitative research. However, this method of sampling is more prone to sampling bias resulting in weaker conclusions drawn about the population. The aim of this sampling method is to develop an initial understanding of the population. The different types of non-probability sampling methods are as . Another sampling method is cluster sampling, in which the population is divided into groups, and one or more groups are randomly selected to be in the sample. Cluster sampling In cluster sampling , the population is divided into subgroups (clusters), and a set of subgroups are selected to be in the sample
random sample types
The following sampling methods are examples of probability sampling: Simple Random Sampling (SRS) . be microcosms, rather than subsections, of the population. Each cluster should be heterogeneous. Additionally, the statistical analysis used with cluster sampling is not only different but also more complicated than that used with stratified .
Another sampling method is cluster sampling, in which the population is divided into groups, and one or more groups are randomly selected to be in the sample. Cluster sampling In cluster sampling , the population is divided into subgroups (clusters), and a set of subgroups are selected to be in the sample.
Note: Random sampling or any other sampling technique can be used to sample members from each stratum. Cluster Sampling: Cluster sampling is often confused with stratified sampling but both these sampling techniques are different from each other. The main difference is that with cluster sampling you have natural groups separating your population.Sampling is the statistical process of selecting a subset—called a ‘sample’—of a population of interest for the purpose of making observations and statistical inferences about that population. Social science research is generally about inferring patterns of behaviours within specific populations. We cannot study entire populations because of feasibility and cost constraints, .Choosing the right sampling method is a pivotal aspect of any research process, but it can be a stumbling block for many. Here’s a structured approach to guide your decision. 1) Define your research goals. If you aim to get a general sense of a larger group, simple random or stratified sampling could be your best bet. For focused insights or .
In snowball sampling, the samples are added to the survey like a chain. The first group of survey subjects is chosen by the researcher, and then the subsequent set of participants is added to the .
grad coach sampling methods
5 de mar. de 2019 · Oct 18, 2021. 41. Oct 4, 2021. 42. Sep 27, 2021. Get the latest Player Stats on Iga Swiatek including her videos, highlights, and more at the official Women's Tennis Association website.
4 sampling methods in statistics|four types of sampling methods